What Do Your Results Indicate About The Importance Of Population Size As An Evolutionary Force
Genetic Migrate
In small, reproductively isolated populations, special circumstances be that can produce rapid changes in gene frequencies totally independent of mutation and natural selection. These changes are due solely to risk factors. The smaller the population, the more susceptible it is to such random changes. This phenomenon is known as genetic drift.
In order to get a better understanding of the potential upshot of population size on development, information technology is useful to deport out a simple money flipping experiment. The expectation is that heads will plough upwardly fifty% of the time because there are just ii sides to a coin--heads and tails. If you flip a money 10 times, information technology may or may not result in 5 heads.
![]() Coin flipping experiment . Take a coin out of your pocket. Flip it 10 times and record the results.
Coin flipping experiment . Take a coin out of your pocket. Flip it 10 times and record the results.
Repeat the experiment twice. Calculate the percentage of times the coin came up heads in each of
your three experiments and, finally, in all of your experiments combined. What did you learn?
The more times that you flip your coin, the more likely information technology will approach the expected 50% heads. If you do information technology an infinite number of times, information technology volition exist 50%. In other words, when a sample is very small, the probable event may not occur. Equally the sample increases in size, it will go progressively closer to it.
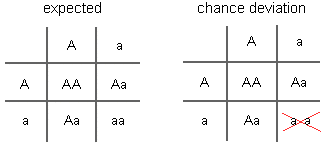
This kind of divergence from the expected effect with small samples too occurs in genetic inheritance when breeding populations are very small. For example, when women and their mates are both heterozygous (Aa) for a trait, nosotros would expect that 25% of their children will be homozygous recessive (aa). By risk, nevertheless, a particular couple might non have whatever children with this genotype (every bit shown below in the Punnett square on the right).
| | |
| thousand enotypes of children | g enotypes of children |
Unless other families have an unpredictably large number of homozygous recessive (aa) children for this trait to counter the random difference, the population's gene puddle frequencies will change in the management of having fewer recessive alleles--genetic drift will occur .
The internet effect of genetic migrate on a small population's gene pool tin exist rapid evolution, as illustrated in the hypothetical inheritance patterns shown below. Notation that the cherry-red trait dramatically increases in frequency from generation to generation. It is important to remember that this tin can occur independent of natural selection or any other evolutionary mechanism.
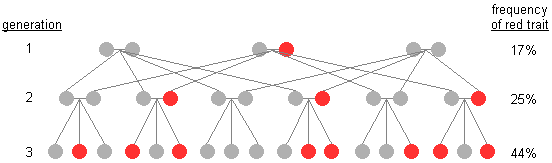 |
| Rapid genetic drift over three generations |
Such distorting statistical anomalies occur regularly. In small populations, they can have a rapid, meaning effect on genetic pool frequencies of subsequent generations. In large populations, nevertheless, they are ordinarily neutralized by other families having children with countering genotypes.
Since genetic drift is measurably constructive only in pocket-size populations, it must have played a major role in the early on stages of human development when our populations were tiny. Withal, even in large societies, such as the United States today, there are small, culturally isolated communities like the Amish and Dunkers of rural Pennsylvania and the Midwest that are mostly closed breeding groups. In such sub-populations, genetic drift is still an important evolutionary mechanism.
Founder Principle
 |
Some other of import minor population effect is known as the founder principle or founder effect. This occurs when a small-scale amount of people have many descendants surviving subsequently a number of generations. The consequence for a population is often high frequencies of specific genetic traits inherited from the few common ancestors who first had them.
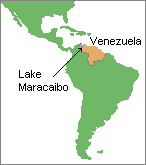
In the Lake Maracaibo region of northwest Venezuela, for instance, there is an extraordinarily high frequency of a severe genetically inherited degenerative nerve disorder known as Huntington'due south disease . Approximately 150 people in the expanse during the 1990's had this rare fatal condition and many others were at high risk for developing it. This disease usually does not strike until early middle historic period, after most people have had their children. Withal, Huntington's can occur much earlier. About 10% of its victims develop symptoms when they are younger than xx years old. In that location is no cure for this disease, simply at that place has been a exam for its genetic marker available since 1993. All of the Lake Maracaibo region Huntington's illness victims trace their beginnings to a woman named Maria Concepci�n Soto who moved into the area in the one9th century. She had an unusually large number of descendants and was therefore the "founder" of what is now a population of nigh xx,000 people with a high take chances of having this unpleasant genetically inherited trait.
 |
Annotation: Huntington's disease is non unique to the Lake Maracaibo region. Information technology occurs throughout the earth at relatively low rates. About 200,000 people in the The states (.07% of the population) take information technology. Perhaps, the virtually well-known victim of Huntington's was the American folk song author and performer Woody Guthrie.
Another example of the founder effect has been discovered among the 16-18,000 Old Society Amish people of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. They are descended from a few dozen individuals belonging to an Anabaptist sect in Federal republic of germany who migrated to Pennsylvania during the early on 1700'due south. Over the last xl years of the 20th century, 61 babies with an extremely rare fatal genetic disorder known every bit microcephaly ![]() were born to 23 Amish families. All of these families are descendants of a single Amish couple nine generations ago. They were the founders of the population with the genes for microcephaly today.
were born to 23 Amish families. All of these families are descendants of a single Amish couple nine generations ago. They were the founders of the population with the genes for microcephaly today.
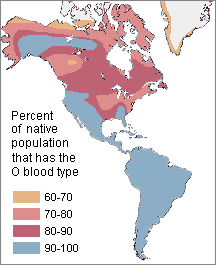
It is likewise possible to find the results of a founder event even though the original ancestors are unknown. For example, South and Cardinal American Indians were well-nigh 100% type O for the ABO blood organisation and 100% positive for the Rh blood system. Since nix in nature seems to strongly select for or against blood types, it is likely that most of these people are descended from a pocket-sized ring of closely related "founders" who also shared these traits. They migrated into the region from the north, probably by the end of the last Ice Age.
Bottleneck Effect
In many species, there accept been catastrophic periods acquired past rapid dramatic changes in natural pick, during which most individuals died without passing on their genes. The few survivors of these evolutionary "bottlenecks" and then were reproductively very successful, resulting in large populations in subsequent generations. The event of this bottleneck event is the boggling reduction in genetic diversity of a species since most variability is lost at the time of the bottleneck.
Bottlenecking also occurs at times in human populations as a result of major epidemics and catastrophic storms, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions. An example of this occurred on the pocket-sized Micronesian island of Pingelap in the Western Pacific. In 1775, a draft killed at least 90% of its people, thereby eliminating nigh of the genetic variation. I of the 20 survivors was a homo named Nahnmwarki Mwanenised. He had achromatopsia, a very rare genetically inherited recessive middle status that causes full color blindness and extreme sensitivity to lite. Six generations later, virtually 5% of the island'southward population had achromatopsia. All of those who had it were descendents of Nahnmwarki Mwanenised. By comparing, only 1 in 33,000 people in the Us have information technology. Not just did the Pinegleapese experience a dramatically reduced genetic diversity as a outcome of the 18th century storm, but unfortunately that surviving gene pool contained the genes for achromatopsia, making this an example of both the bottlenecking effect and the founder principle.
Copyright � 1997-2014 by Dennis O'Neil. All rights reserved.
illustration credits
What Do Your Results Indicate About The Importance Of Population Size As An Evolutionary Force,
Source: https://www2.palomar.edu/anthro/synthetic/synth_5.htm
Posted by: westlijjoing.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Do Your Results Indicate About The Importance Of Population Size As An Evolutionary Force"
Post a Comment